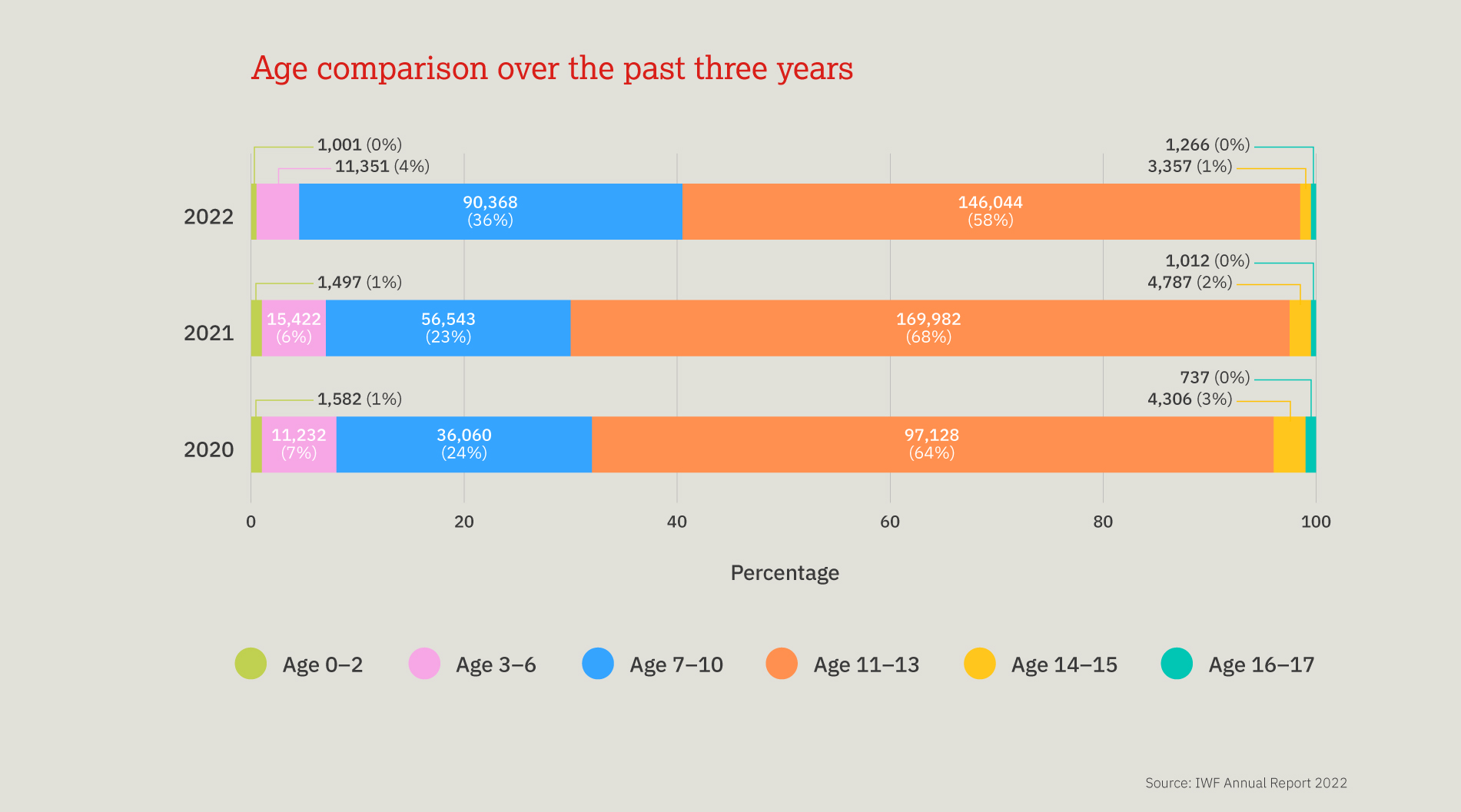
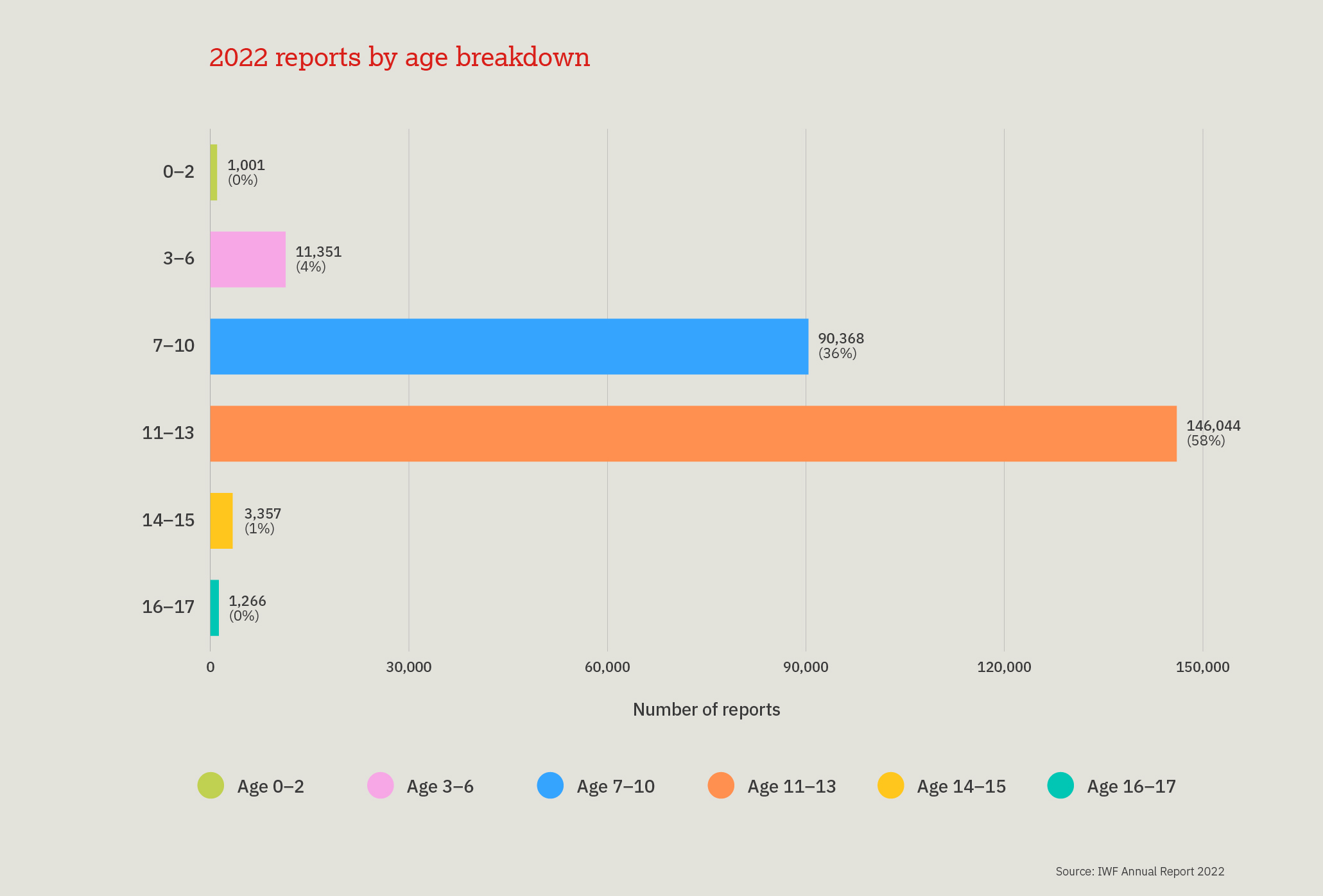
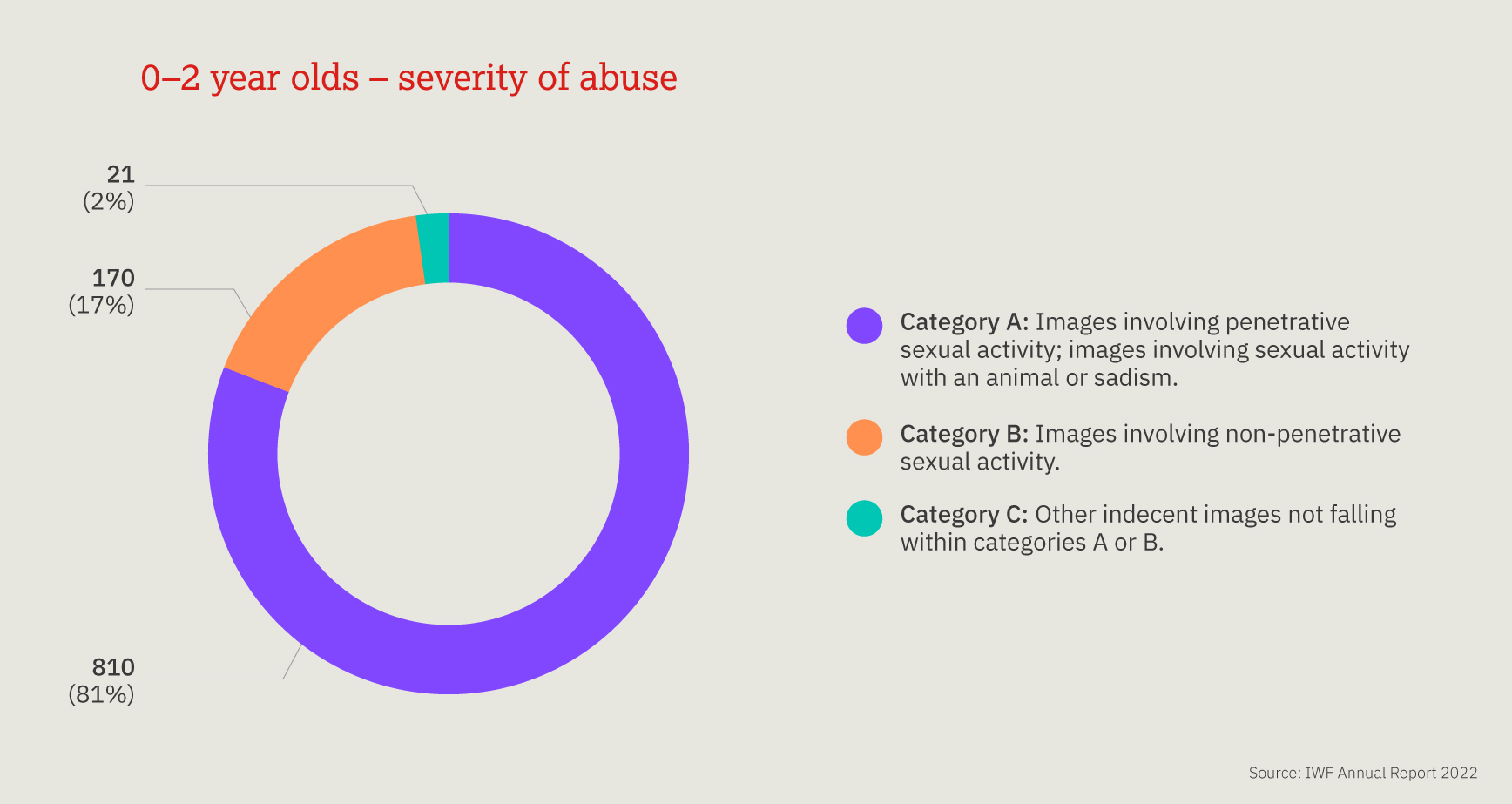
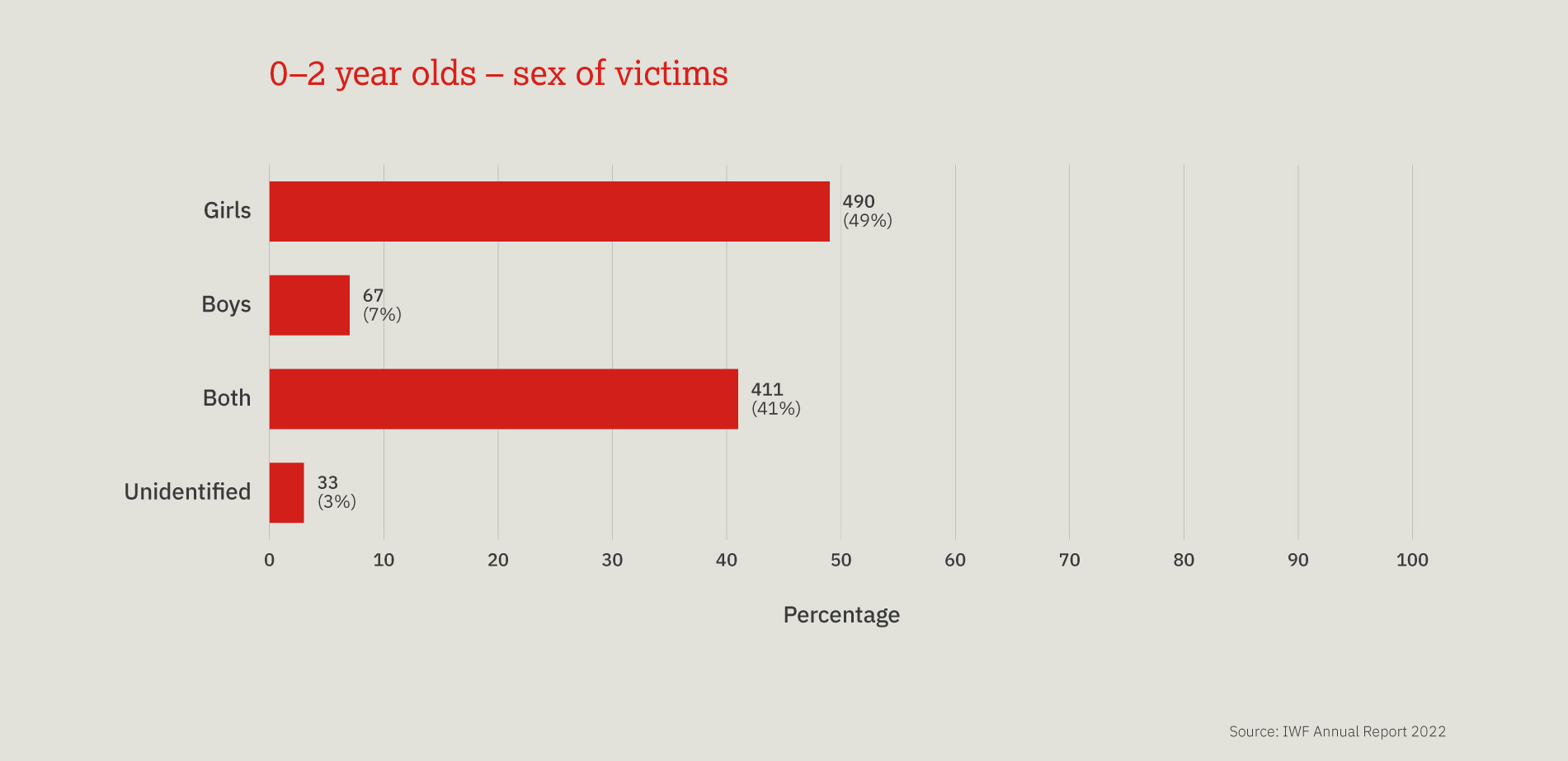
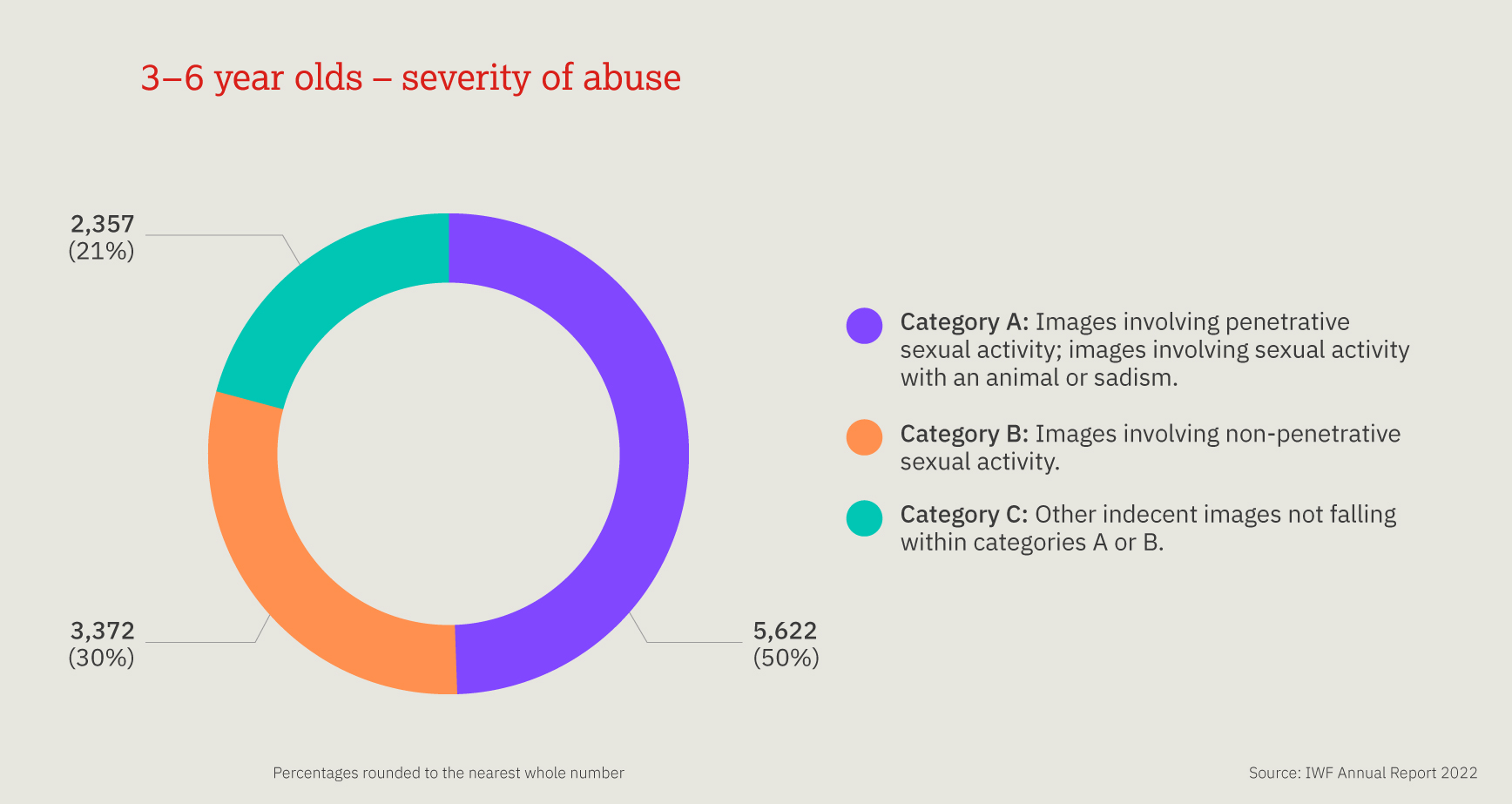
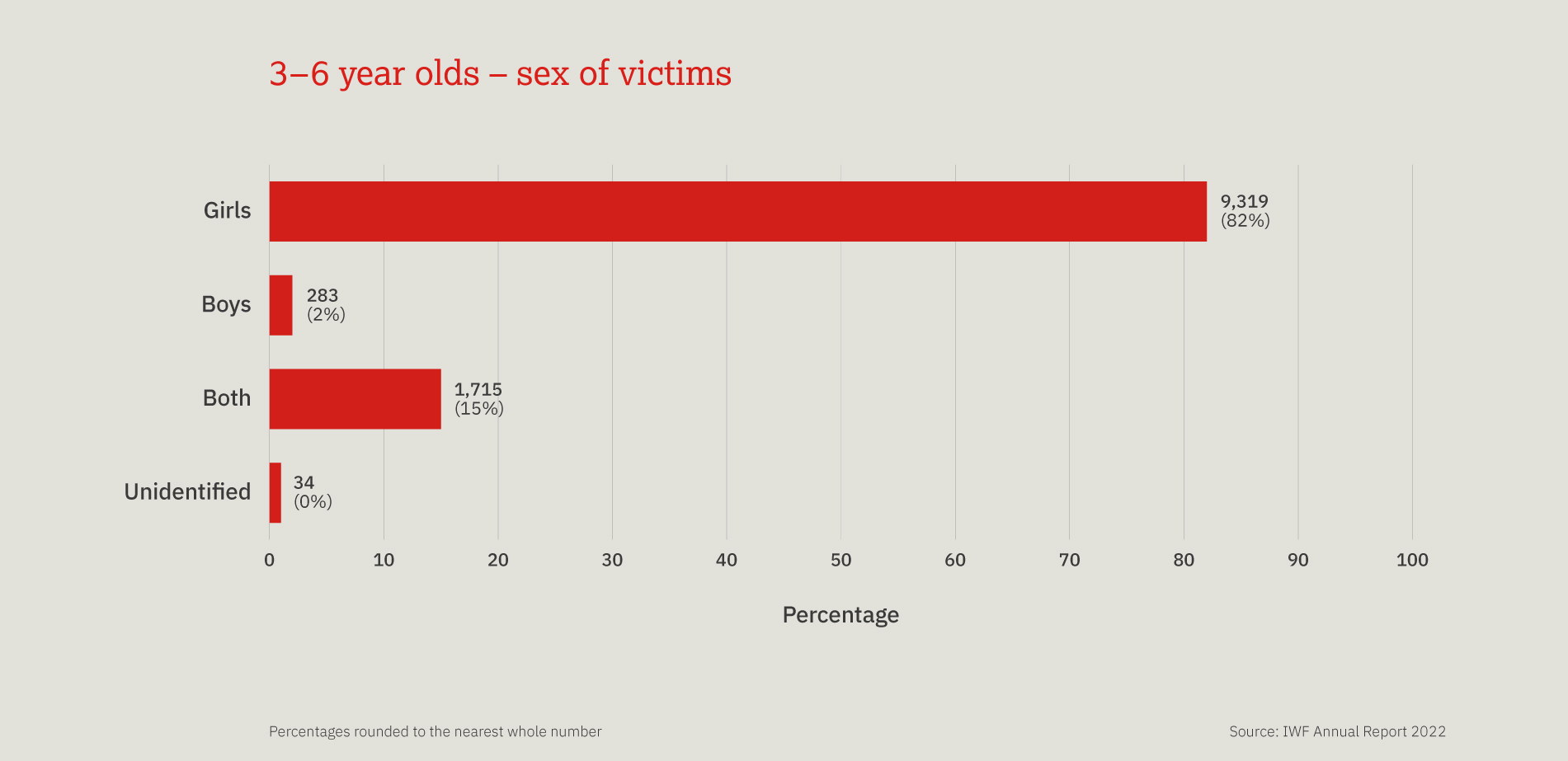
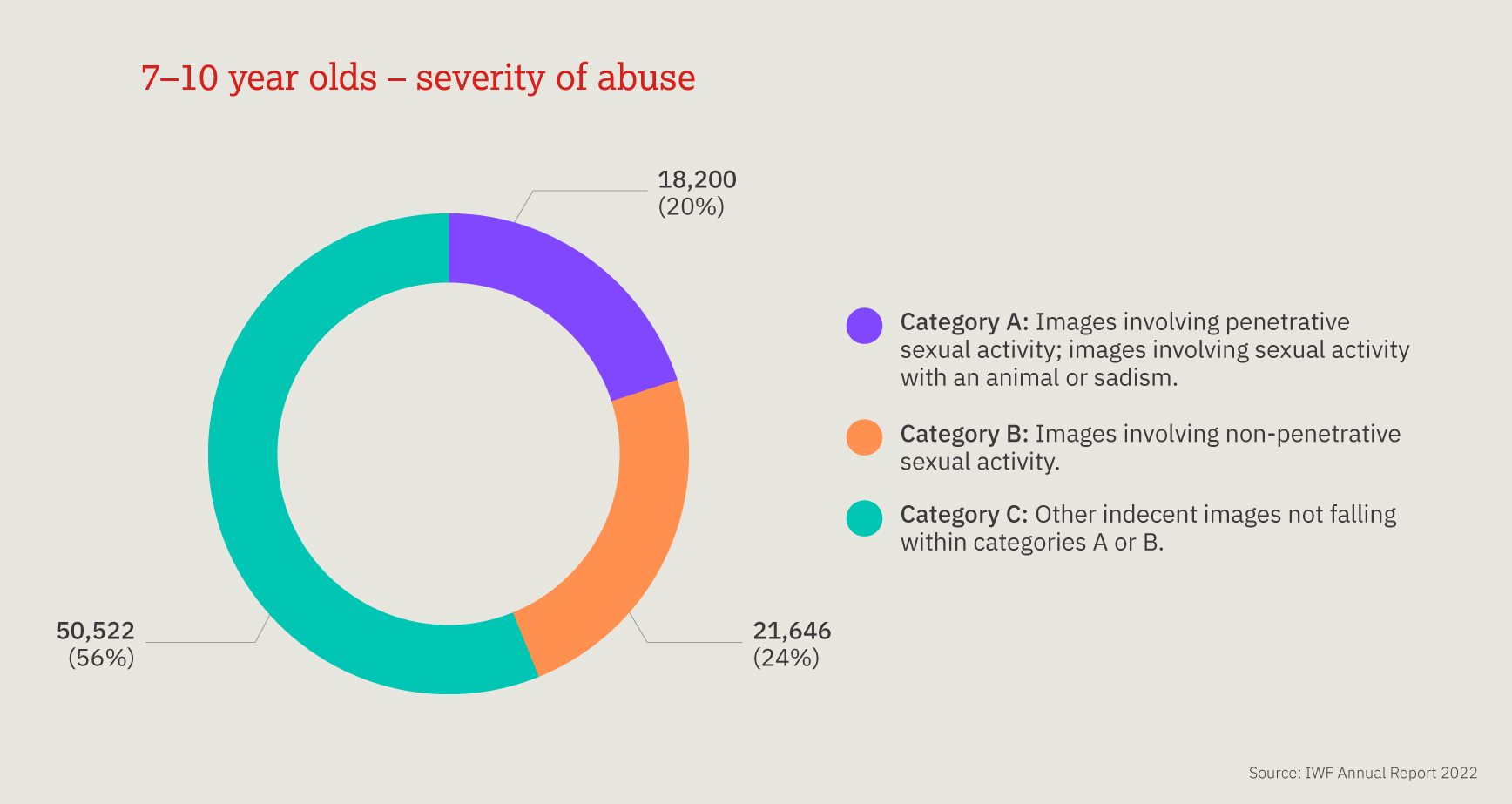
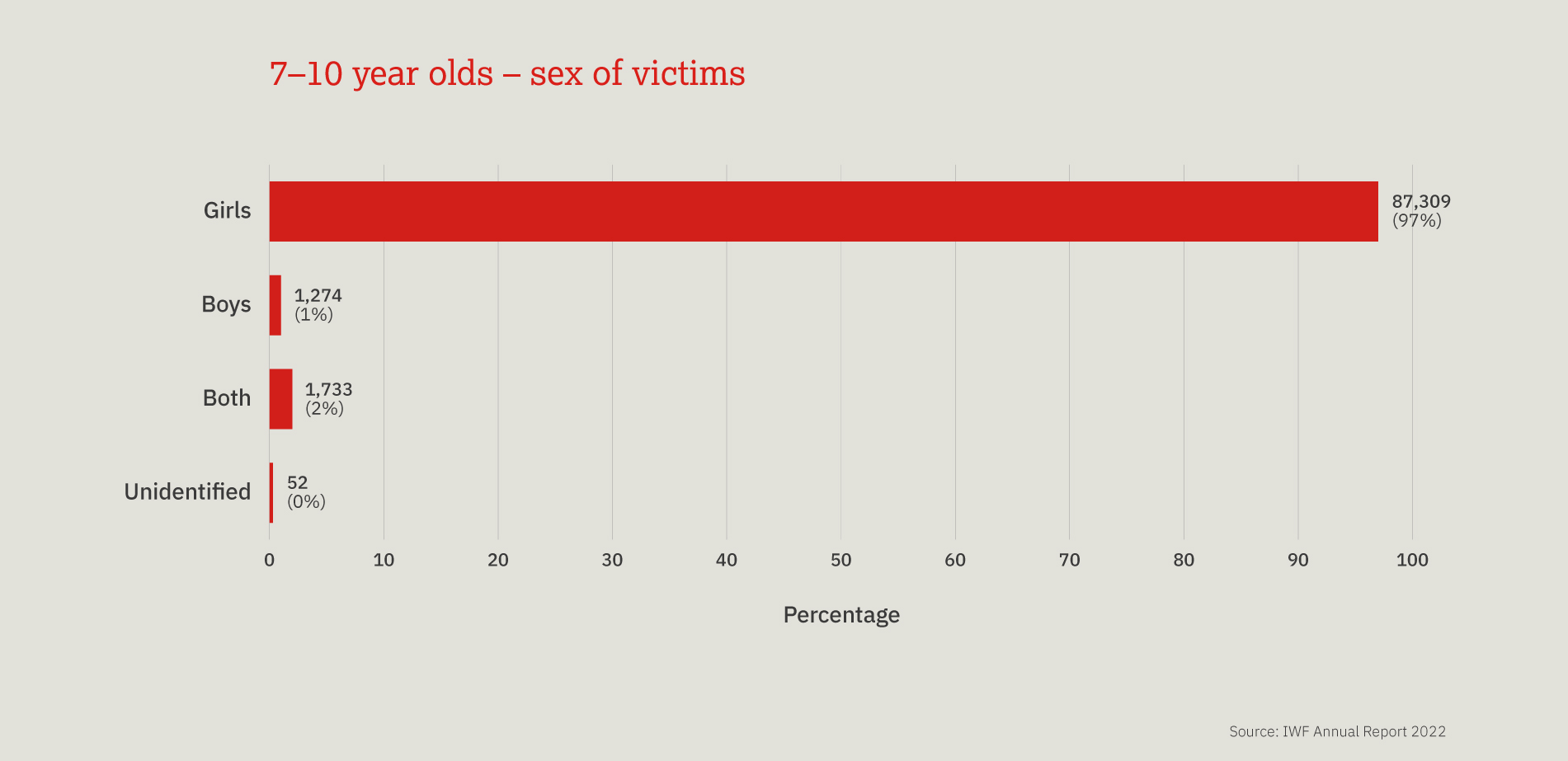
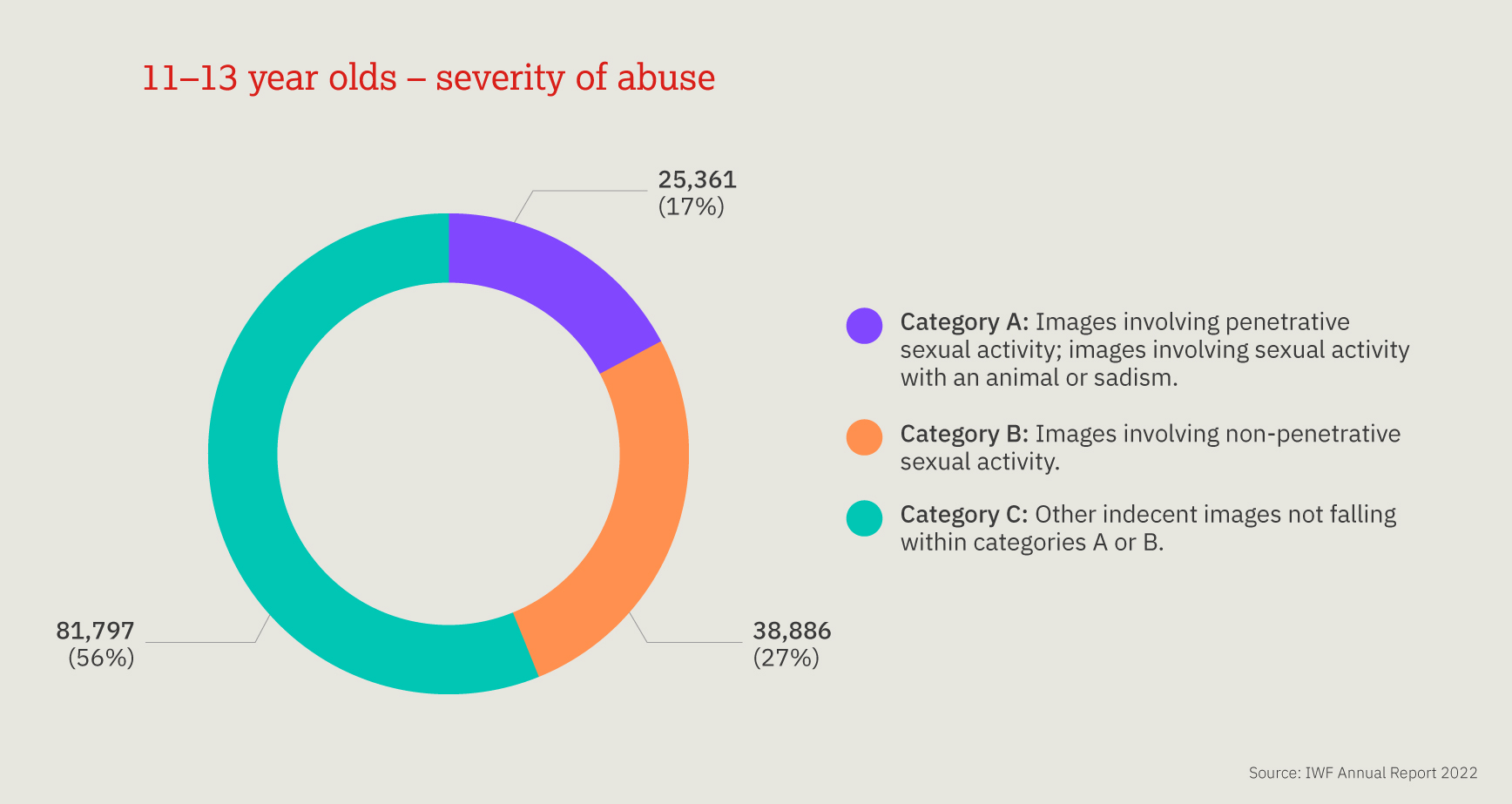
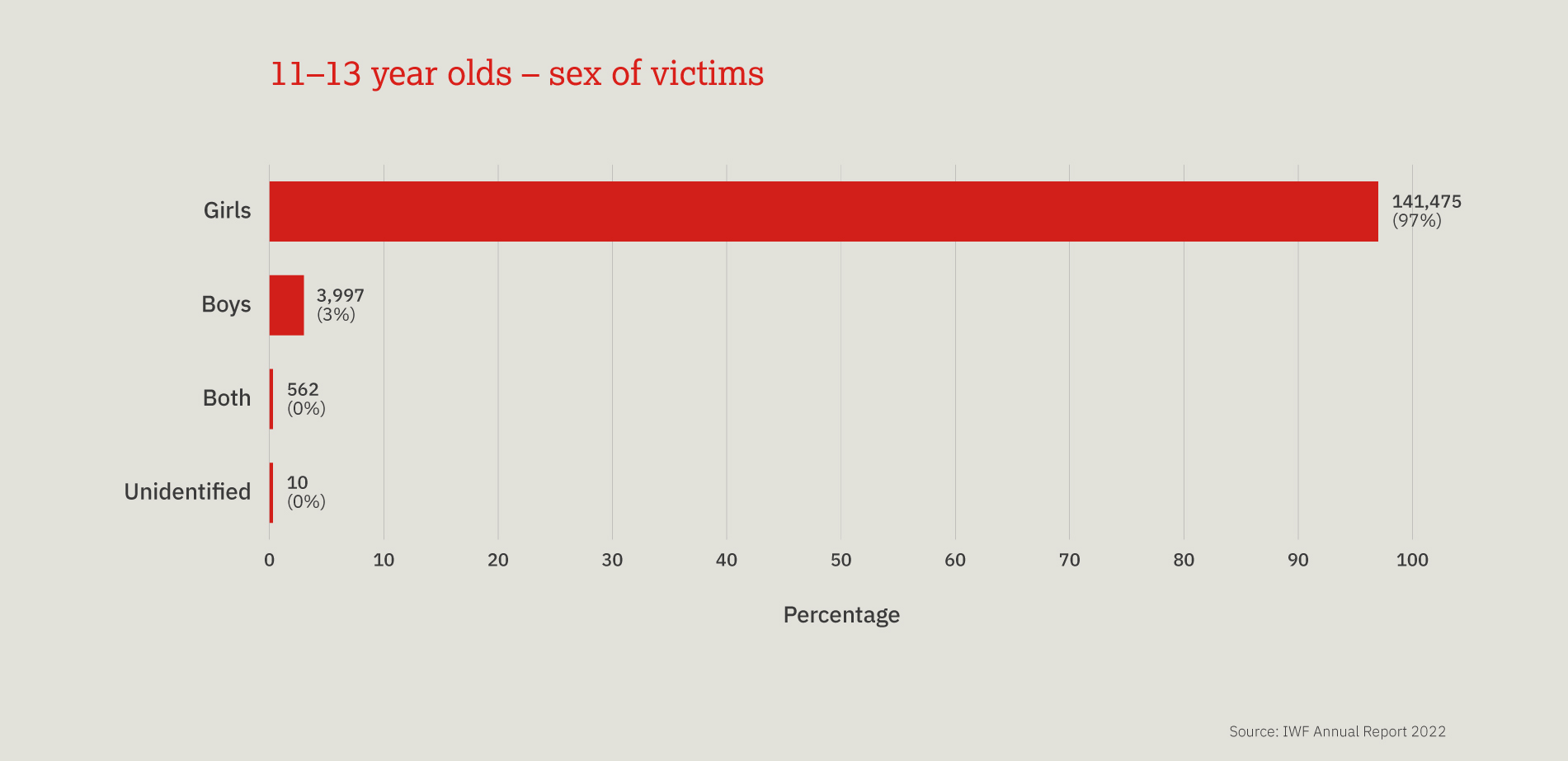
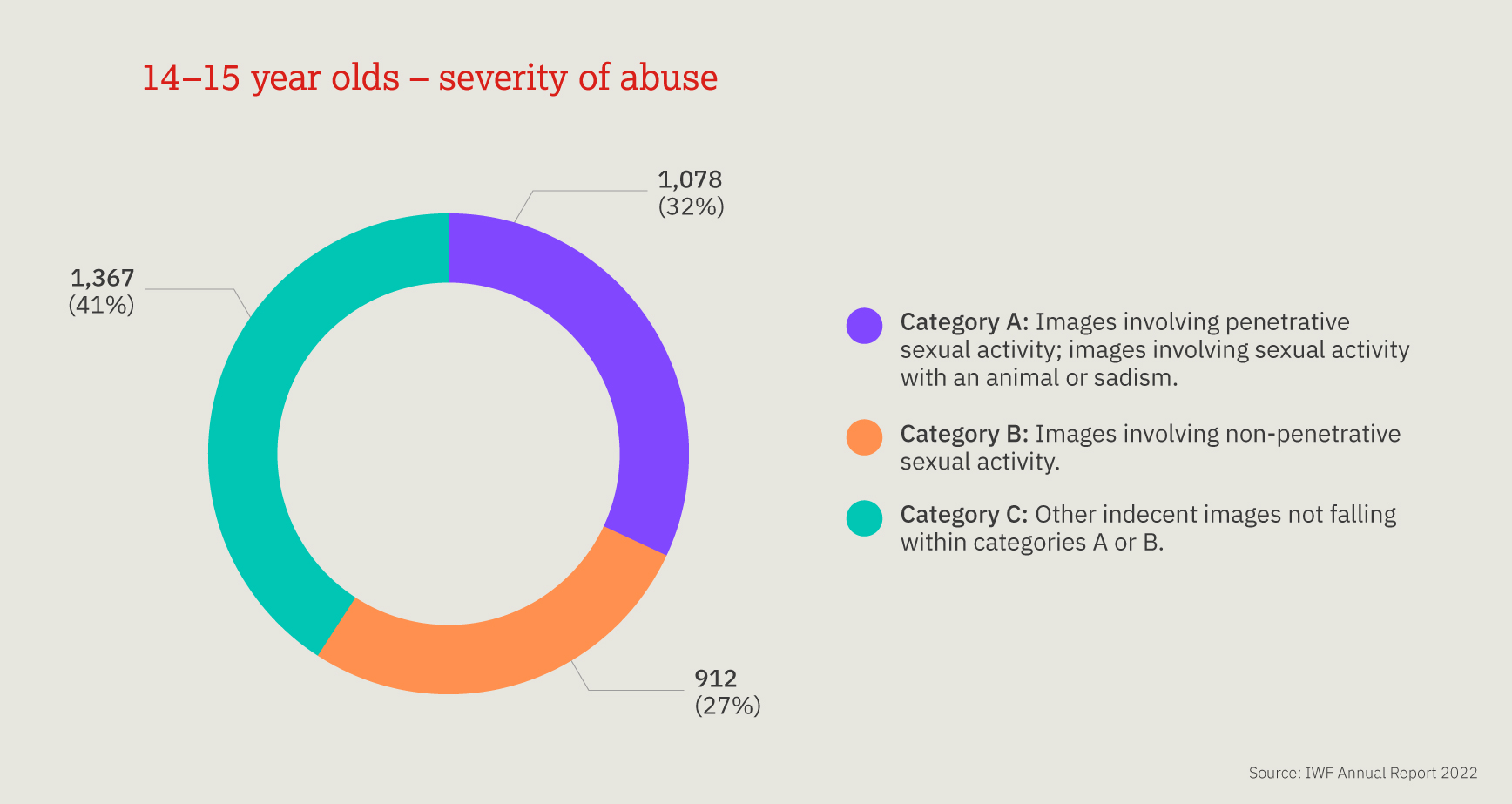
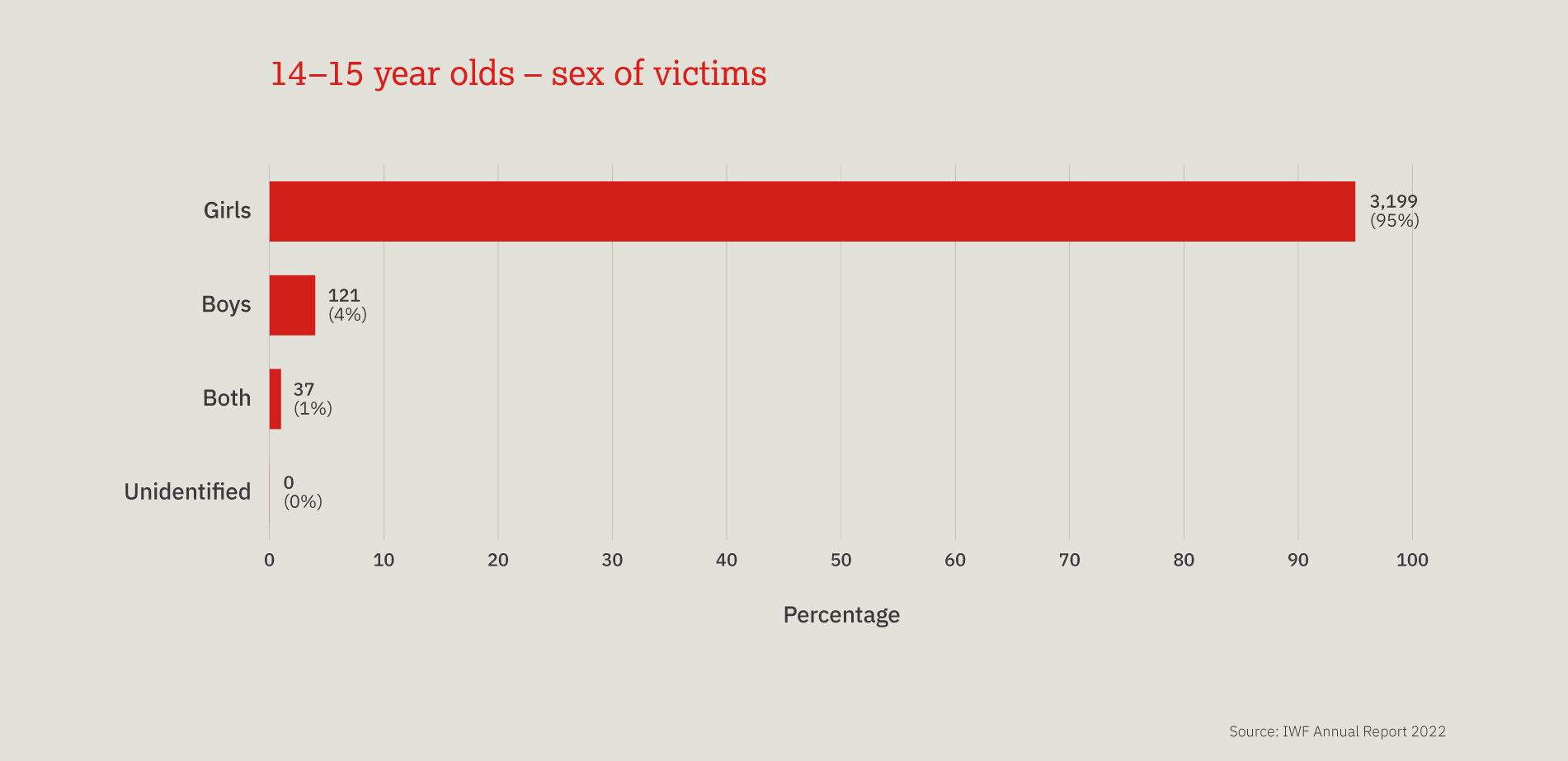
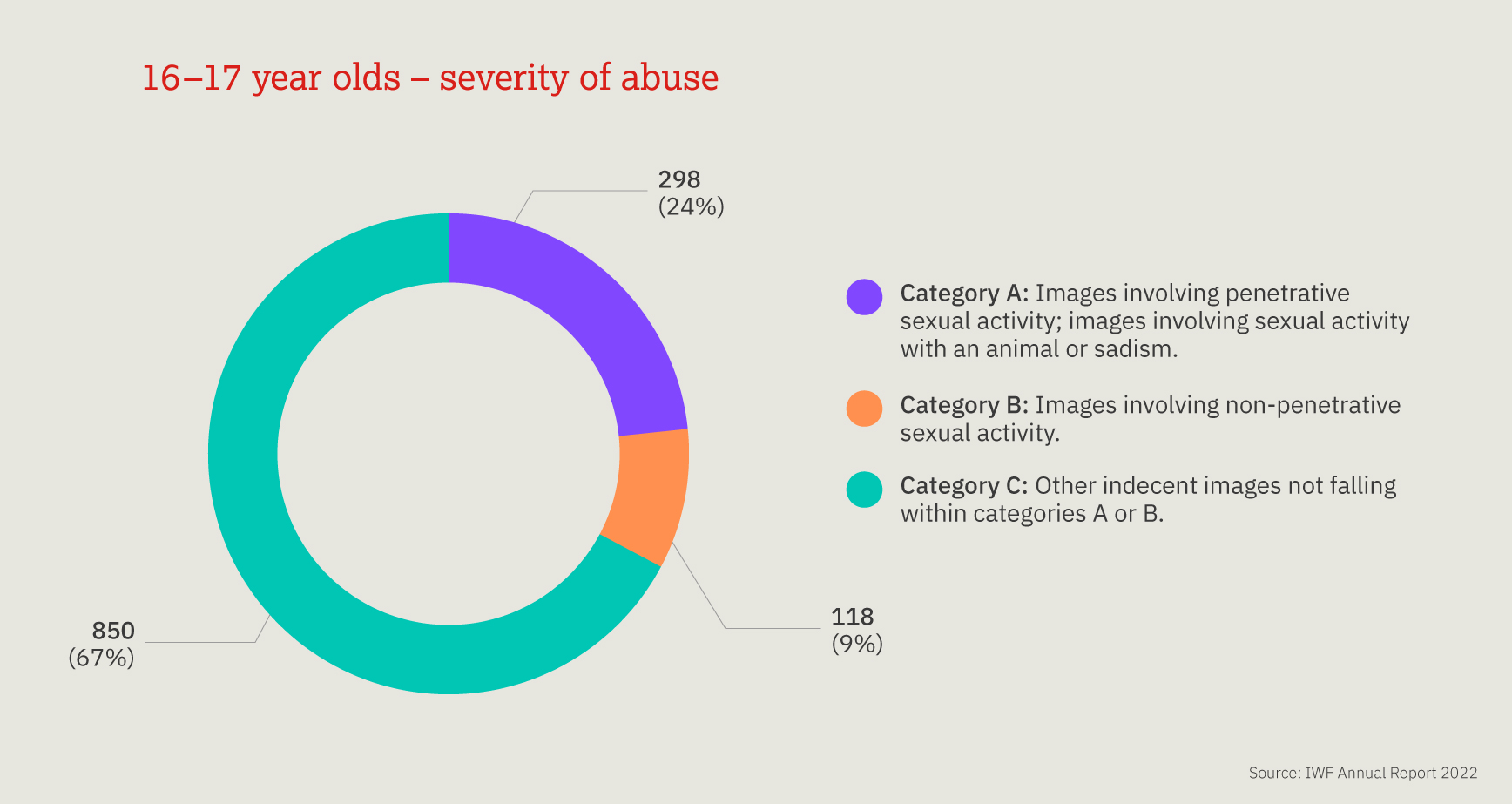
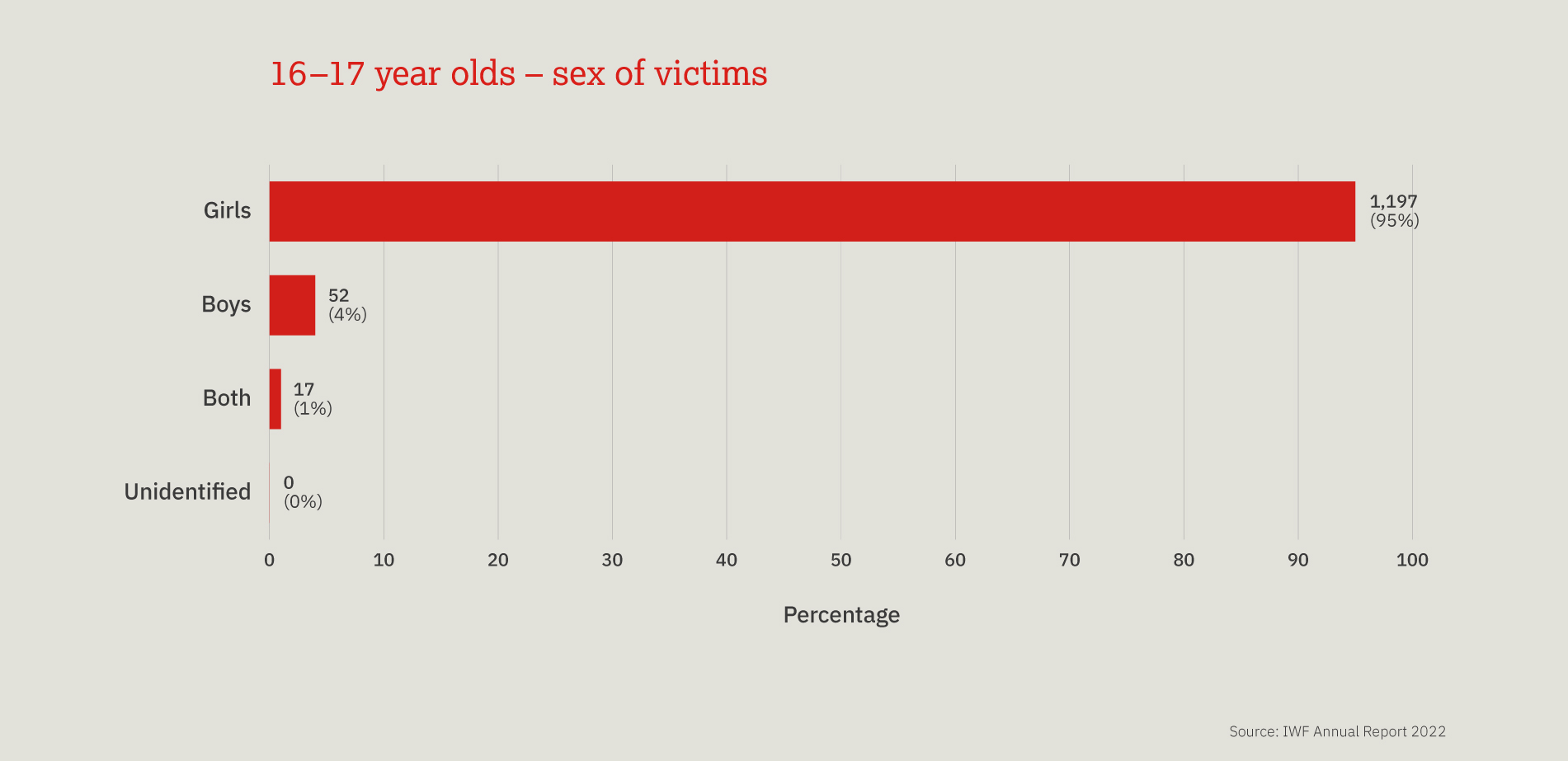
This chart provides a three-year look at the number, and proportion, of child sexual abuse URLs identified by IWF analysts split by age of the youngest child seen in any image upon that URL.
Over the past three years, children aged 11-13 are most often seen, however a 10 percentage point decrease was noted in 2022, compared to 2021. We also noted a 13 percentage point increase in the number of 7-10 year old children.